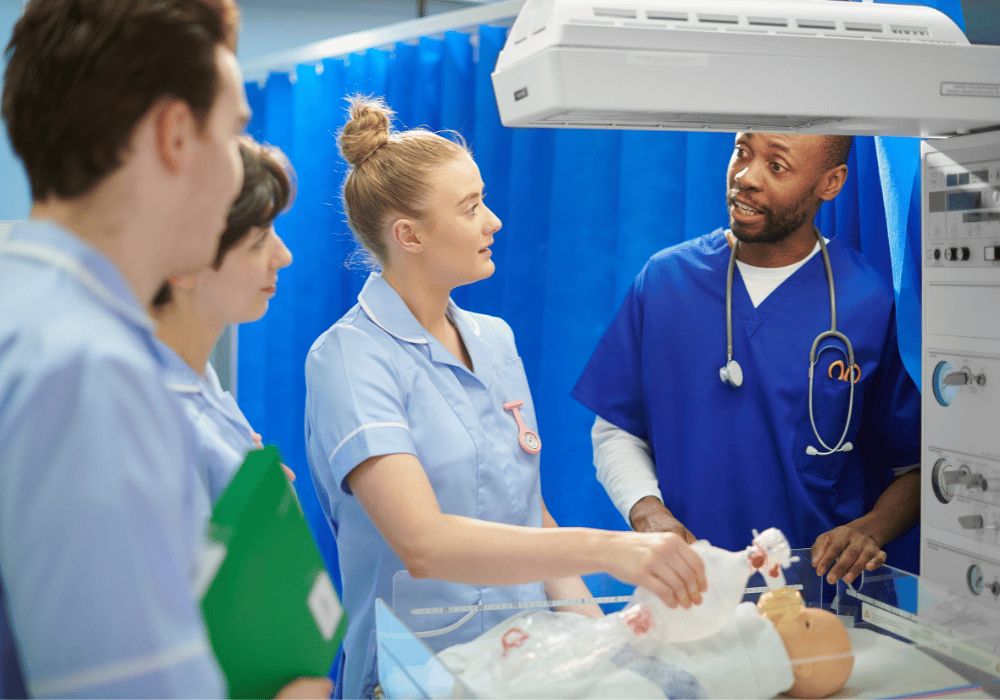
Whether it’s responding to a sudden cardiac arrest, handling a traumatic injury, or managing a large-scale disaster, medical professionals are often faced with high-stakes, time-critical decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.
Read more: All About Medical Emergency SimulationsGiven these pressures, it’s paramount that medical professionals are trained to the highest standards possible. Traditional methods of teaching and learning, while foundational, often fall short in terms of preparing individuals for the reality of emergency situations. This is where medical emergency simulations emerge as a vital tool, replicating real-life scenarios to provide hands-on experience without real-world consequences.
The Importance of Effective Training for Medical Professionals
Human lives are in the balance when it comes to medical emergencies, and the decisions made by healthcare providers can be the ultimate factor in patient outcomes. Through history and understandings in modern analysis highlight that training and experience have a significant role in these outcomes. Hence, delivering effective training is a moral imperative that the medical profession upholds with the utmost seriousness.
Medical emergency training is not just about the technical skills and procedures; it’s also about the cognitive processes that take place under stress and the collective response of a medical team. An effective training program must take into account the complexity of emergency situations, the integration of various medical disciplines, and the coordination of care among multiple healthcare professionals.
Role of Medical Emergency Simulations
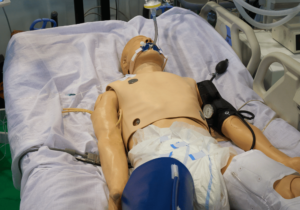
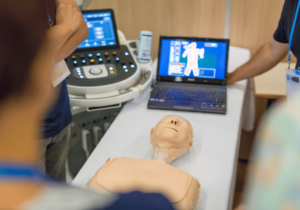
Medical emergency simulations are scenarios designed to replicate real medical situations. The scenarios can vary from a singular patient crisis to a major disaster. They create an immersive learning environment that is essential for medical professionals to practice and master complex skills. These simulations, often conducted in controlled environments, such as simulation centers, bridge the gap between theoretical training and practical application. They allow learners to make critical decisions, perform procedures, and manage unexpected developments in a safe setting.
By their nature, simulations force trainees to engage with the material in a hands-on, experiential way, which has been proven to enhance retention of knowledge and development of procedural skills.
Types of Medical Emergency Simulations
Simulations in the medical field come in various formats, each with its unique affordances and applications. Here are the primary types of medical emergency simulations.
High-Fidelity Simulations
High-fidelity simulations involve the use of sophisticated computerized mannequins programmed to exhibit lifelike physiological responses, including breathing, speaking, and complex patient monitoring. These mannequins can be programmed to escalate or de-escalate the scenario based on the actions taken by the learners, providing an adaptive and realistic experience.
Virtual Reality Simulations
Virtual reality (VR) takes simulation to another level, providing 3D, computer-generated environments that can be explored and interacted with by a person using a VR headset. VR simulations in medical training offer the advantage of accessibility and allow for practice in scenarios that may be hazardous or extremely rare in real life.
Standardized Patient Simulations
Standardized patients are real people trained to portray patients in a medical situation. They offer a more interpersonal, human element to simulations, and are particularly effective in training for communication skills and building empathy in medical professionals.
Tabletop Simulations
Tabletop simulations involve a group of individuals who discuss and develop responses to a particular emergency scenario. These are interactive and can complement other types of simulations by encouraging discussions around roles, responsibilities, and procedures without the presence of high-tech equipment.

