
Menu
Close
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) and first responders play a critical role in saving lives. Their ability to perform under intense pressure is only as strong as their training allows. Recognizing this, Canada has seen a shift in how EMS and first responder training is delivered, with simulation-based methods emerging as a game-changing tool.
From lifelike scenarios to advanced virtual reality technologies, simulation is bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world emergencies. This blog explores how simulation is revolutionizing Canadian EMS training, from its benefits and real-life examples to the challenges that still need addressing. If you’re an EMS professional, educator, or policymaker, here’s why simulation deserves your attention.
Simulation-based training has become a core facet of medical and emergency response education worldwide. Here’s why it is particularly suited to the unique demands of Canadian EMS:
 1. Enhancing Critical Decision-Making Skills
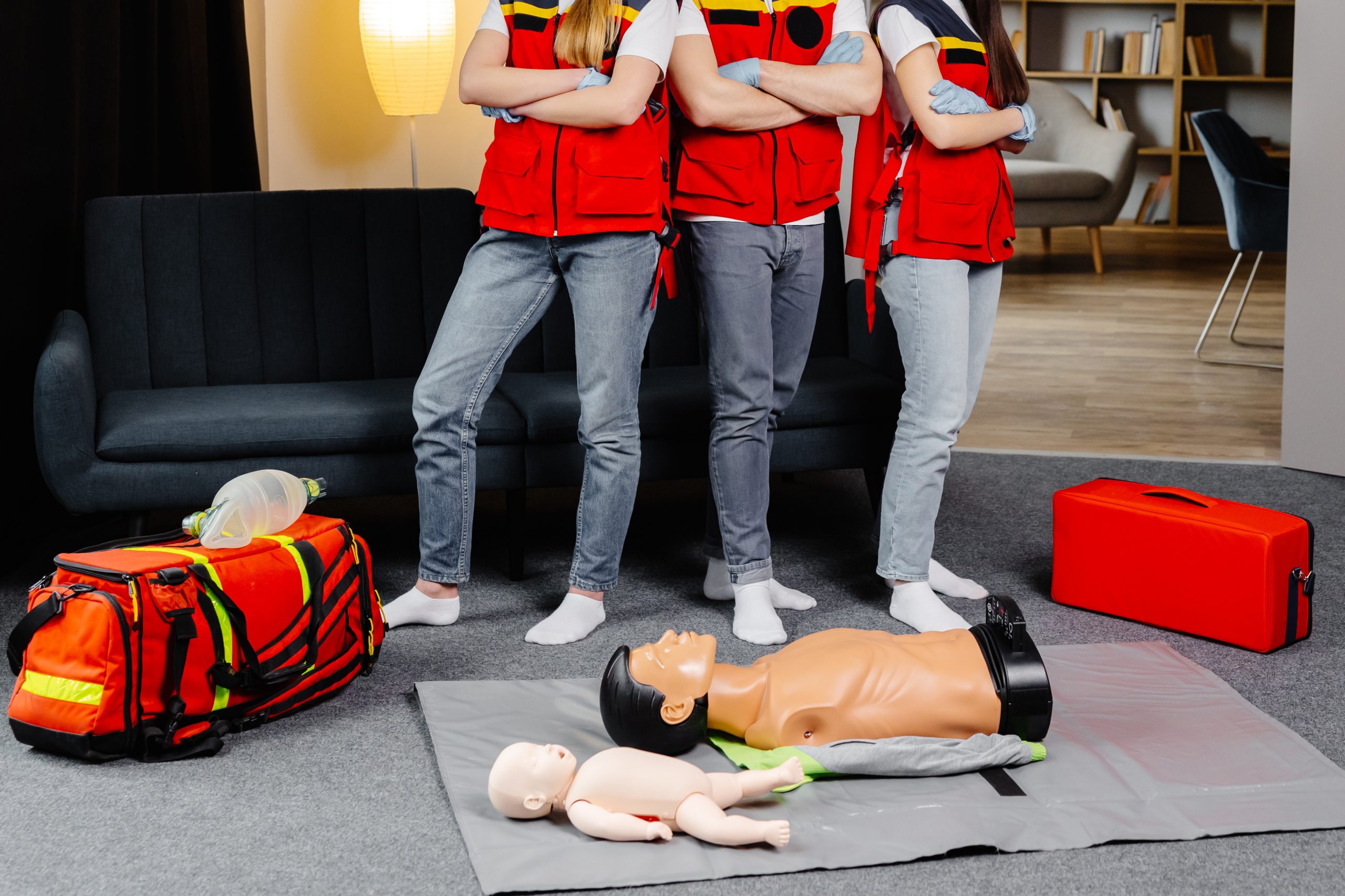
1. Enhancing Critical Decision-Making SkillsMedical emergencies are unpredictable. A split-second decision can mean the difference between life and death. Simulation mimics real-life pressure scenarios, such as cardiac arrests or multi-vehicle collisions, enabling EMS workers to practice critical decision-making in high-stakes situations. This better equips them for real-world emergencies.
Whether it’s learning how to intubate a patient or handle a defibrillator, simulation provides hands-on practice in a controlled, stress-free setting. EMS trainees gain confidence by repeatedly practicing procedures until they achieve mastery.
Emergency responses often involve multiple first responders working together. Simulation-based training allows teams to practice communication and coordination. Scenarios like disaster response drills bring EMS professionals, firefighters, and police officers together, ensuring everyone is on the same page during live events.
The “learning by doing” approach has limitations in traditional EMS education, primarily because practice with real patients poses ethical and safety concerns. Simulation eliminates this risk, allowing trainees to learn from mistakes without jeopardizing patient safety.
Whether working in remote northern communities or bustling urban centres, Canada’s EMS practitioners face varied challenges. Simulations can be customized to address regional needs, such as handling wilderness rescues or responding to extreme weather conditions.
The technology behind simulation training can range from simple mannequins to advanced virtual reality systems. Here’s a look at the tools being used across Canada.
The backbone of simulation training, high-fidelity mannequins mimic human anatomy and physiology. Devices like CAE Healthcare’s iSimulate or Laerdal Medical’s ALS mannequins allow trainees to measure vitals, perform CPR, intubate, and even monitor responses to administered drugs. These mannequins are widely adopted by Canadian EMS programs for their realistic response systems.
VR and AR are increasingly being integrated into Canadian EMS training. Programs like SimX offer immersive virtual environments where responders can practice responding to large-scale emergencies, such as mass casualty accidents or active shooter situations. This not only builds operational preparedness but also provides scalable training for teams.
Wearable technology is also gaining traction. Devices like TraumaFX suits enable actors to simulate realistic injuries. These tools create hyper-authentic training scenarios, where EMS professionals can practice applying tourniquets or treating severe wounds.
Recognizing the need to extend training access to underserved areas, many programs in Canada have adopted mobile simulation units. These are trucks or buses equipped with simulation stations that travel to rural or remote regions, providing hands-on training to EMS teams in isolated areas.
Several Canadian provinces are leading the way in incorporating simulation-based training into EMS education. Here are a few standout examples:
JIBC is renowned for its state-of-the-art simulation labs, featuring high-fidelity mannequins and fully immersive scenarios designed to challenge even experienced responders. Their Trauma Simulation suite has consistently received accolades for its ability to mimic real-world emergencies in a safe, controlled setting.
Alberta has been a pioneer in deploying mobile simulation units equipped with advanced medical equipment. These units travel across the province, ensuring that EMS teams in rural areas have access to the same quality of training as their urban counterparts.
Toronto Paramedic Services collaborates with police and fire departments for joint simulation exercises that emphasize teamwork and communication. Their Mass Casualty Incident (MCI) training drills are regarded as the gold standard for multi-agency preparedness.
Montreal’s McGill University Health Centre uses neonatal simulation technology to train responders on how to manage emergencies involving newborns. Their program addresses a unique but critical area often overlooked in traditional EMS training.
Despite its advantages, incorporating simulation training into EMS programs comes with challenges. Here’s a breakdown of common hurdles and actionable solutions:
 1. High Costs
1. High CostsChallenges:
Solutions:
Governments and educational institutions can collaborate with private companies to secure funding. Applying for grants specifically focused on healthcare innovation can help offset costs.
Challenges:
Solutions:
Mobile simulation units bridge the gap by taking training directly to underserved areas. Additionally, VR-based solutions can democratize access to training by eliminating geographical barriers.
Challenges:
Solutions:
Change management strategies, including emphasizing the benefits of simulation in professional development and job performance, are key. Successful pilot programs can also demonstrate measurable outcomes, building trust among stakeholders.
Simulation is no longer a luxury; it’s becoming a necessity. As the demand for highly skilled EMS professionals grows, so will the role of innovative training techniques. Future trends to watch include:
Canada has already taken impressive steps in adopting simulation-based EMS training. By continuing to invest in this technology, the nation can ensure its emergency responders are prepared for challenges both known and unknown. If you’re in the field of EMS or education, now is the time to explore how simulation tools can elevate training programs. The future is bright, and simulation is leading the way.